Crypto has a lot of different use cases, for example NFTs, GameFi, Memes or DeFi. This article is a brief overview of DeFi.
DeFi is short for decentralized finance, where financial products become available on a public decentralized blockchain network. It aims to use technology to remove intermediaries between parties in a financial service.
Points 5-7 are much less common, it’s still a long way to use this widely. But everything depends/is build on top of each other, for example is credit lending or exchanges not possible without a certain value.
1. Value
If we speak about a decentralized value, it’s mostly about bitcoin. Bitcoin is the oldest crypto currency with the biggest market cap. These characteristics in combination with bitcoin’s architecture leads to a high level of trust. I’ve written a couple of articles on how bitcoin works, you can start here.
2. Transfer
| Task | CeFi | DeFi |
| Send 50$ to Person A | Bank transfer, Paypal, Stripe, … | decentralised transfer (Mining, Staking) |
The benefits of a centralized system is that transactions can happen really fast and sometimes even without a fee. However, you still need to trust the central party.
Like I written earlier, with DeFi this level of trust becomes obsolete. But who has the voting right to verify transactions?
In DeFi, there must be a cost factor to get voting rights. Otherwise, a Sybil attack would be possible. The most used concepts are:
- Proof-of-Work (Mining)
- Proof-of-Stake (Staking)
With Proof-of-Work (PoW), you solve complex mathematical problems. The costs are computer devices and electricity power. It comes with 2 benefits, transaction fees and block rewards.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) isn’t about solving a mathematical problem. Instead you “lock” coins into a box. Therefore, the costs for a voting right are the coins of the currency itself. Like in PoW, you get transaction fees and block rewards. The annual reward is called APR, with compound interest it’s called APY.
3. Exchanges
Decentralized Exchanges (DEX), like Uniswap, Sushiswap or Pancakeswap are built on top of the blockchain, called 2nd layer solutions. They introduced new concepts like liquidity mining.
But how is a decentralized swap possible?
In centralized exchanges, there is an order book with all the buyers and sellers. If two parties match a certain price, a swap is possible. You can also see the liquidity and how deep the price request are going.
However, a decentralized order book wasn’t that successful, because it requires a website to display the book. The website comes as a central point which provides a weak point.
Sidenote: Every system that comes with a central point provides an opportunity for regulations. So pay attention to projects which are based on, for example a website.
But in fact, you don’t necessarily need a order book with supply and demands. DEX are using pools, every pool consists of a pair, for example BTC and ETH.
Let’s say there is a pool with 1 BTC and 15 ETH, therefore 1 BTC equals 15 ETH. If somebody says: ” I think BTC is more valuable, I want to change my 1.5 ETH into BTC”. Now, he adds his 1.5 ETH to the pool.
Although the ratio was 1/15, he doesn’t get 0.1 BTC. As soon as he adds his amount, the ratio goes up as well. Therefore, he will receive ~0,091 BTC minus the transaction fees.
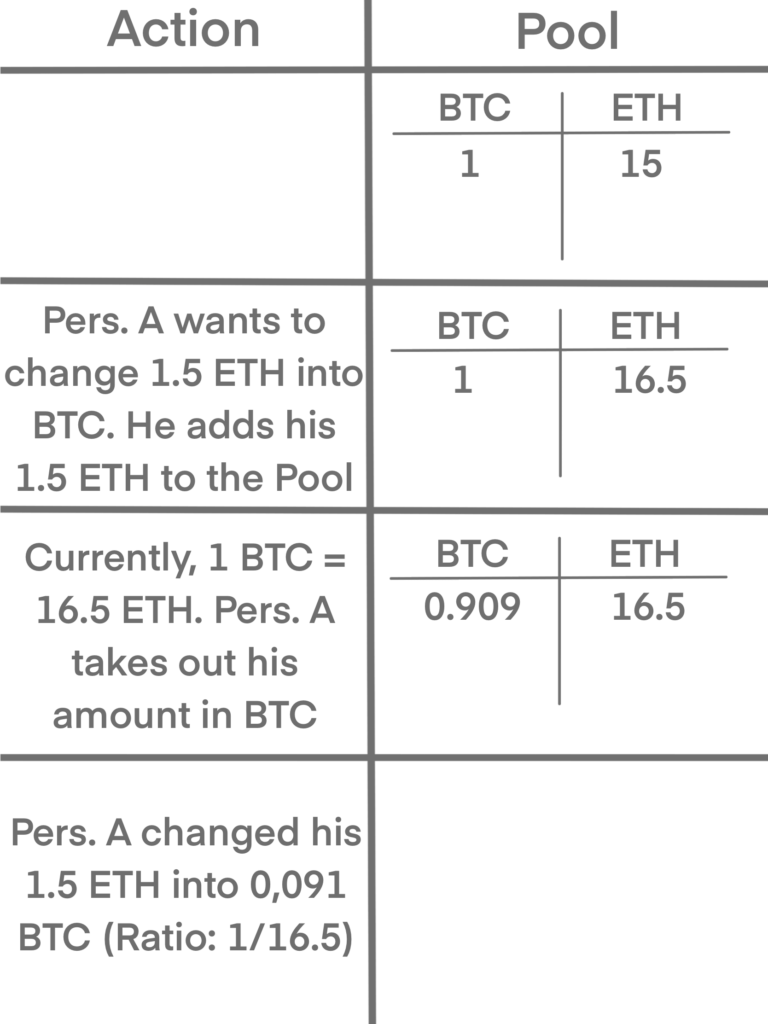
Of course you want to have a lot of liquidity in the pool, because it reduces the margin of the swap. Liquidity is specified as the TVL (Total Value Locked), which is provided by the liquidity miners. Liquidity miners add both parts in the same amount of the current ratio. In compensation, they receive the transaction fees and block rewards.
Impermanent loss:
Liquidity miners see their amount in Liquidity Mining Tokens. At the beginning, the value of these tokens is defined in an algorithm. If we take our previous case, there is a pool with 1 BTC and 15 ETH. For example, this would equal 10 Liquidity Mining Tokens. If you provide an additional 1 BTC and 15 ETH, you will collect 10 Tokens.
From now on, it’s the same concept as staking. You will receive transaction fees and block rewards on the tokens. Since there are only 20 tokens and you own 10 of them, you get 50% of all rewards.
But what happens if the ratio changes and you want to get out?
In our example: Someone changed 15 ETH for BTC, the pool currently contains 45 ETH and 1,34 BTC. But there are still 20 Liquidity Mining Tokens and you own 10 of them. If you go out now, you also get 50% of both sides.
| Before: | After: |
| 1 BTC and 15 ETH | 0,67 BTC and 22,5 ETH (+ rewards) |
Depending on the current exchange rate, we may have made a loss – called the impermanent loss.
The chance of an impermanent loss rises when the price of one part goes much higher/lower than the price of the other part. It’s important to calculate the chances (rewards) and risks (impermanent loss) before providing liquidity.
4. Credit
In the credit business, doesn’t matter if it’s BTC/EUR/USD, you need someone who takes the credit.
But what are they going to do with that credit?
They have two options, shorting the market or use it for leverage.
Obviously you get a reward if you lend your money. But if the majority thinks the price of a currency will go down, the rewards will rise. That’s because less people are willing to lend their currency than people taking a credit.
5. Tokenization
The use of digital tokens came about as a means of replacing sensitive data with a non-sensitive digital equivalent.
There are some examples for central tokenization, like the Lichtenstein Token Container Model (TKM). In the TKM, you can e.g. deposit an Apple stock with a token on a blockchain. This token now has the same rights and benefits as the Apple stock itself. In fact, it’s basically a security token.
However, the whole market of security tokens has still a lot of regulatory issues:
- who is allowed to store security tokens
- unified rules between nations
- secondary market
- prospectus requirements
So what about decentralized tokenization?
Apparently, there wouldn’t be any regulatory issues. But a stock, like our apple stock, is not decentral.
The solution is similar to a CFD, where there isn’t an actual stock. Instead the stock is created synthetically.
To create our apple stock, we give an amount of e.g. BTC and ETH into a Vault. Vaults can store cryptocurrencies just like regular wallets. Moreover, they can prevent crypto from being immediately withdrawn.
Let’s say there is a vault with 1000$ in BTC, ETH and USD. Now the vault let you create a decentralized token with 10% of that amount. If an apple stock costs 200$, you own a half of a stock (which is represented by the token).
Sidenote: Somehow, the blockchain needs to know the current price of a stock. This can be done with an oracle, but it needs to be server less. Otherwise, the prices can be manipulated.
But how I’m going to profit from rising prices?
You don’t. If you’re doing this, you bet against Apple and on BTC, ETH and USD. Imagine a scenario where Apple goes down to 100$. The token can be redeemed only for the same percentage within the vault. Since the stock go down, you receive less BTC, ETH and Dollar.
But it needs an interest rate, which creates an urgency to redeem the token.
However, why should anyone take these risks of shorting a stock including an interest rate?
Because you’re able to start liquidity mining with it. The stock (token) can be part of a pool, it’s the same process as explained earlier.
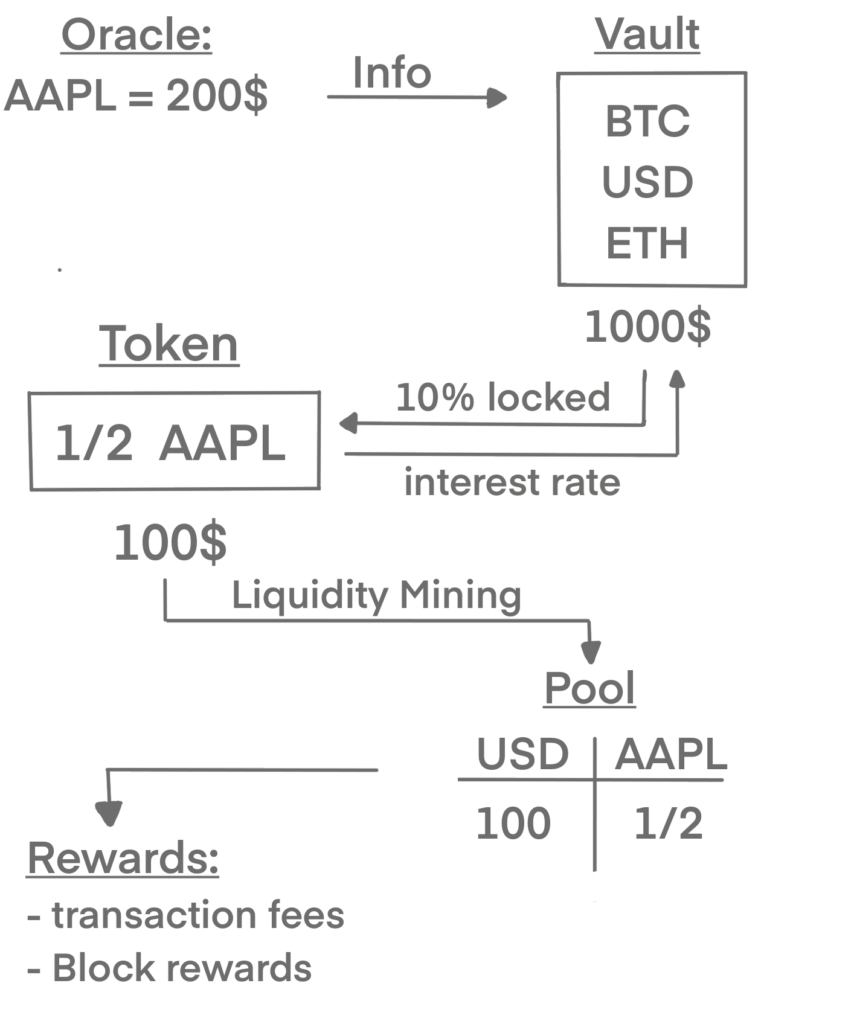
Important notes:
- The stock price in the pool will converge to the price provided by the oracle
- there can be an Impermanent loss between the rewards and the interest rates.
- if less people are willing to create a (stock) token, interest rates will fall and rewards will rise
- every stock/commodity/… can be directly traded into another, you don’t have to go back to dollar and paying any fees to banks
- everybody can access it
6. Prediction markets
Prediction markets can also be organized in a DEX. The pool contains a stable value, like USD and the bet you want to take, for example futures or options. The bet has connections to other DEX pools.
7. Reputation
First of all, it needs all the 6 points above to make reputation possible. But someday, based on your undeleteable blockchain history, you receive reputation. Institutions or other people can now calculate the risks of lending you money. This enables financial products like unsecured loans.